AWS Direct Connect and AWS VPN enable secure communication between the client's on-premises infrastructure and the AWS Cloud services. However, they differ in terms of their features, capabilities, and the use cases they cater to.
This article will compare the two services, discuss their features, pros, and cons, and define the possible use cases for each one.

There are multiple ways of connecting your infrastructure to Amazon Web Services, with each option leveraging either AWS Direct Connect or a VPN, or a combination of both. The options are equally viable, but each caters to a different use case and corresponds to different business requirements.
The following table lists the key differences between AWS Direct Connect and AWS VPN:
| Feature | AWS Direct Connect | AWS VPN |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Provides a dedicated connection between on-premises infrastructure and AWS services, bypassing the public Internet. | Provides a secure, encrypted remote access to AWS resources using the public Internet. |
| Network Type | A physical, dedicated connection. | A virtual private connection (VPC) over the Internet. |
| Bandwidth | Ranging from 1-10 Gbps. | Limited by the available Internet bandwidth. |
| Latency | Very low latency due to being a dedicated connection. Choosing the closest region lowers latency additionally. | Higher latency than Direct Connect because the connection uses the public Internet. |
| Cost | More expensive than VPN because dedicated infrastructure is required. | More cost-effective because it uses existing Internet connections. |
| Setup Complexity | More complex to set up and it requires physical connections. | Easier to set up since it is configurable through software. |
| Security | The connection is more secure as there is no exposure to the public Internet. | VPN relies on encryption and security measures over the public Internet. |
The sections below cover the two connectivity options in detail, listing the pros and cons and key use cases.
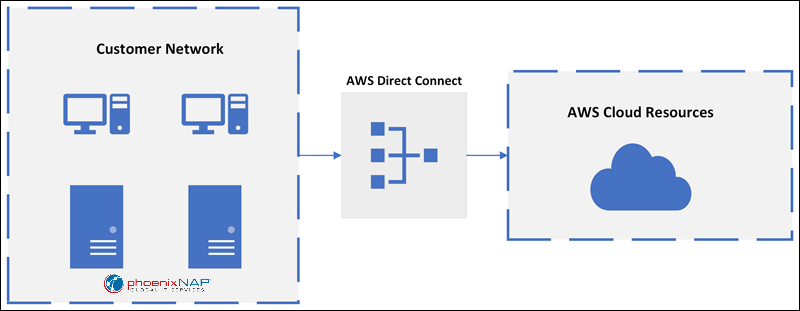
AWS Direct Connect is a dedicated network connection that bypasses the public Internet to create a secure connection between your on-premises infrastructure and AWS. The connection occurs over a fiber-optic Ethernet cable, with one end connected to your router and the other connected to an AWS router.
The Direct Connect connections are high-speed, low-latency connections, ideal for scenarios where substantial amounts of data need to be transferred with consistent network performance. AWS provides different Direct Connect locations across the world to allow users to select the one closest to them.
Note: phoenixNAP allows you to establish a Direct Connect connection using its enterprise-grade data centers in multiple locations around the world. Learn about how can you set up and configure AWS Direct Connect with phoenixNAP.
The connection is suitable for businesses that need secure, low-latency connections to AWS services. Although provisioning AWS Direct Connect can sometimes be time-consuming, the result is superior network performance and security.
The following diagram illustrates the Direct Connect connection:
It's important to weigh the pros and cons of AWS Direct Connect before deciding to implement it. The two following lists highlight the key pros and cons of AWS Direct Connect:
Pros
Note: Learn more about different types of cyber attacks and how can they impact your business.
Cons
AWS Direct Connect has many use cases that benefit a wide range of industries. This section explores the most common use cases of AWS Direct Connect.
Use AWS Direct Connect for:
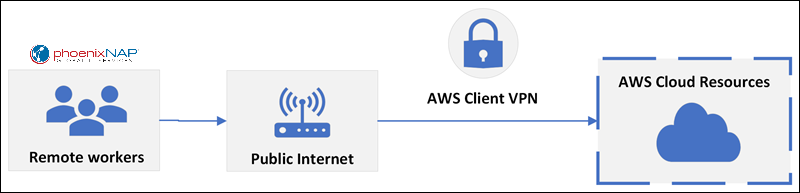
AWS Virtual Private Network (VPN) is an Amazon Web Services offering that allows users to connect their on-premises infrastructure to the AWS cloud using the public Internet. The connection establishes an encrypted tunnel between the client's local network and the VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) in AWS.
The VPN connection utilizes IPSec to establish an encrypted connection, which allows users to securely access their resources as if they were on their own network. AWS VPN also allows users to extend their existing security and management policies to the VPC.
The connection is a great option for businesses that are getting started with AWS as it is easy to set up. The main downside is that it utilizes the public Internet, which means the performance can fluctuate, and that there are some security concerns, despite the encryption.
The following diagram illustrates the AWS VPN connection:
AWS VPN provides a secure and encrypted connection to AWS resources. While it offers numerous benefits to organizations, it also has limitations, making it unsuitable for some use cases.
The following lists contain the pros and cons of AWS VPN:
Pros
Cons
The VPN connection covers a wide range of use cases. This section lists common use cases:
While the two connection options are standalone solutions, they can be combined to leverage the benefits of the IPSec VPN connection and the low-latency high-bandwidth connection of AWS Direct Connect. The combination provides consistent network connectivity with elevated data security and reliability.
In this combination, Direct Connect provides a dedicated, private connection to AWS resources, with lower latency than standard Internet connections. VPN compensates for the lack of encryption by encrypting the traffic. Using AWS VPN to create a secure VPN connection over Direct Connect, businesses create a highly secure and reliable connection to AWS.
AWS VPN and AWS Direct Connect allow you to create a hybrid cloud environment. This combination provides a seamless and secure connection to AWS resources and simplifies network management with overall improved data security.
For example, combining VPN and Direct Connect would be beneficial in a scenario where remote workers need to access an enterprise network securely from various locations in the world. You can use Direct Connect to create a dedicated connection between your data center and AWS resources, while remote workers use VPN to securely access the network from any location.
This article compared AWS Direct Connect and AWS VPN, two connectivity solutions from Amazon Web Services. The comparison included their features, capabilities, and use cases, and listed the pros and cons for each solution.
Use AWS Direct Connect for high performance and compliance requirements, and AWS VPN for scenarios that require flexible and easy-to-manage connectivity. Check out AWS Direct Connect vs. AWS PrivateLink comparison article to see how these two AWS services are different.
If you're considering both Amazon and Microsoft services, our post AWS Direct Connect vs. Azure ExpressRoute will help you make the right choice.